RETINAL DISEASE
TREATMENT
Retinal diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and retinal tears can cause severe and irreversible vision loss. Other retinal diseases include blood vessel obstruction, diabetic eye disease, epiretinal membranes, and macular holes.
Retinal disorders mainly affect individuals above the age of 60 although there are incidences of younger people being affected as well. Screening for these disorders and timely treatment will aid in prevention or limit vision loss.
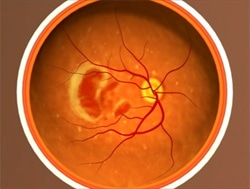
RETINAL LASER THERAPY
Retinal laser therapy can be used to treat retinal tears, diabetic retinopathy, and age-related macular degeneration. If the retina is already detached, a scleral buckle and/or vitrectomy surgery needs to be performed to prevent vision loss.
During retinal laser therapy, a laser is directed at the bleeding blood vessels or retinal tear to heat up the tissue and then seal it. Discomfort during the procedure if any, is minor. It is common for anaesthetic eyedrops to be used to numb the eye during the procedure. The eye specialist may also administer a mild oral sedative to help you relax.
Laser therapy is an out-patient operation, and most can usually return to work the following day.

ADVANCEMENTS IN RETINAL DISEASE TREATMENTS
Many previously incurable retinal problems can now be successfully treated with new medication, technology and procedures:
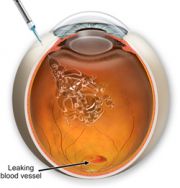
Medication
Wet age-related macular degeneration (abnormal leakage of fluid or blood into the macula) can now be treated by injecting drugs into the eye to stop or slow the progression of the disease. These drugs (e.g., Lucentis, Eylea, or Avastin) are also beneficial in the treatment of other types of macula disorders, such as swelling of the macula (macular edema) caused by diabetes or artery obstruction.
Laser Technology
There have also been advancements in retinal laser technology for the treatment of diabetic eye disease, retinal tears, and other conditions. There are now laser devices, which can provide treatment with lesser discomfort and fewer adverse effects.
Surgical Procedures
In recent years, surgical treatment of retinal detachment, vitreous haemorrhages, and severe diabetic eye disease has also improved. Vitrectomy surgery, for example, can now be performed with smaller, sutureless incisions. This lessens post-operative pain and recovery time.
